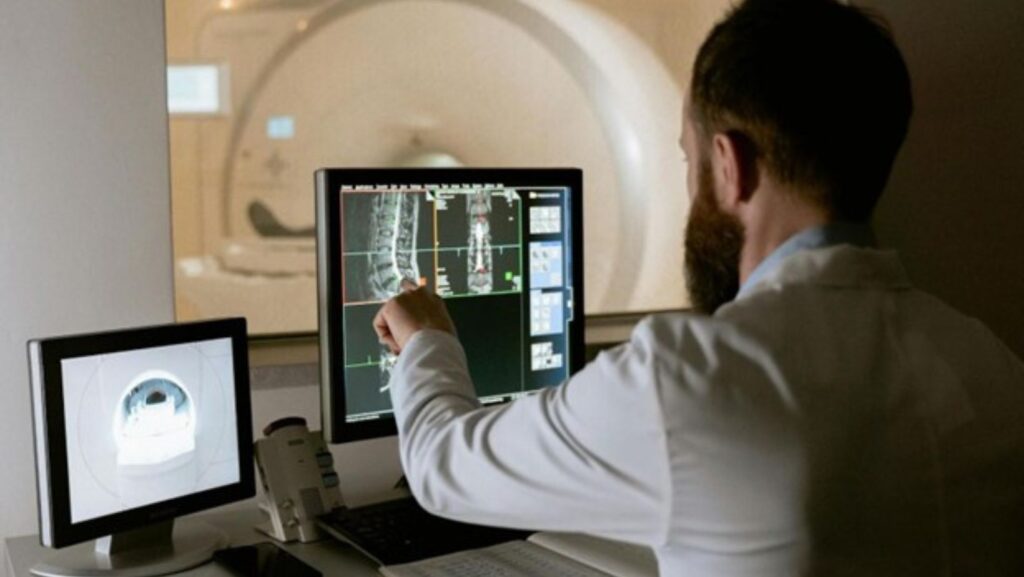
Custom image annotation solutions are revolutionizing healthcare by enabling the creation of precise datasets for AI training. These datasets empower healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses, develop effective treatments, and enhance patient outcomes.
By identifying critical details in medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, image annotation helps train AI models to detect patterns and anomalies with greater accuracy. In this article, we’ll explore the role of custom image annotation in healthcare, including its benefits, challenges, key use cases, and future trends.
About Healthcare Image Annotation
Image annotation involves marking specific parts of a medical image to highlight key features. These annotations help AI systems find similar patterns in other datasets. This improves diagnostic accuracy and enables predictive analysis.
For example:
- X-rays: Identifying fractures, tumors, or infections.
- CT scans: Highlighting organs, blood vessels, or abnormal growths.
- MRIs: Mapping brain anomalies, spinal issues, or soft tissue injuries.
AI in medical imaging relies on annotated datasets for solid results. If the labeling is not accurate, models can misinterpret the data, drawing wrong conclusions. Here, a custom approach is crucial for building effective AI systems in healthcare.
Types of Medical Image Annotations
There are several key types of healthcare image annotation you should know about.
Bounding Boxes
Drawn around areas of interest to isolate specific regions. For example, highlighting a tumor in a chest X-ray.
Polygons
Outline irregular structures for precise localization. Example? Tracing the edges of a skin lesion.
Semantic Segmentation
Labels every pixel, separating the image into distinct regions. Differentiating tissues, organs, and abnormalities in a brain scan is one of the examples.
Key Points
Marks specific coordinates to indicate critical features. Think of mapping skeletal joints in an orthopedic X-ray.
3D Annotations
Adds depth to images and is used for volumetric data like CT scans. 3D annotations can be used for highlighting the volume and shape of a tumor in a CT scan to estimate its size and progression.
Instance Segmentation
It uses object detection and segmentation to find and separate structures in an image. A prime example: separate and label lung nodules in a CT scan to tell benign from malignant growths.
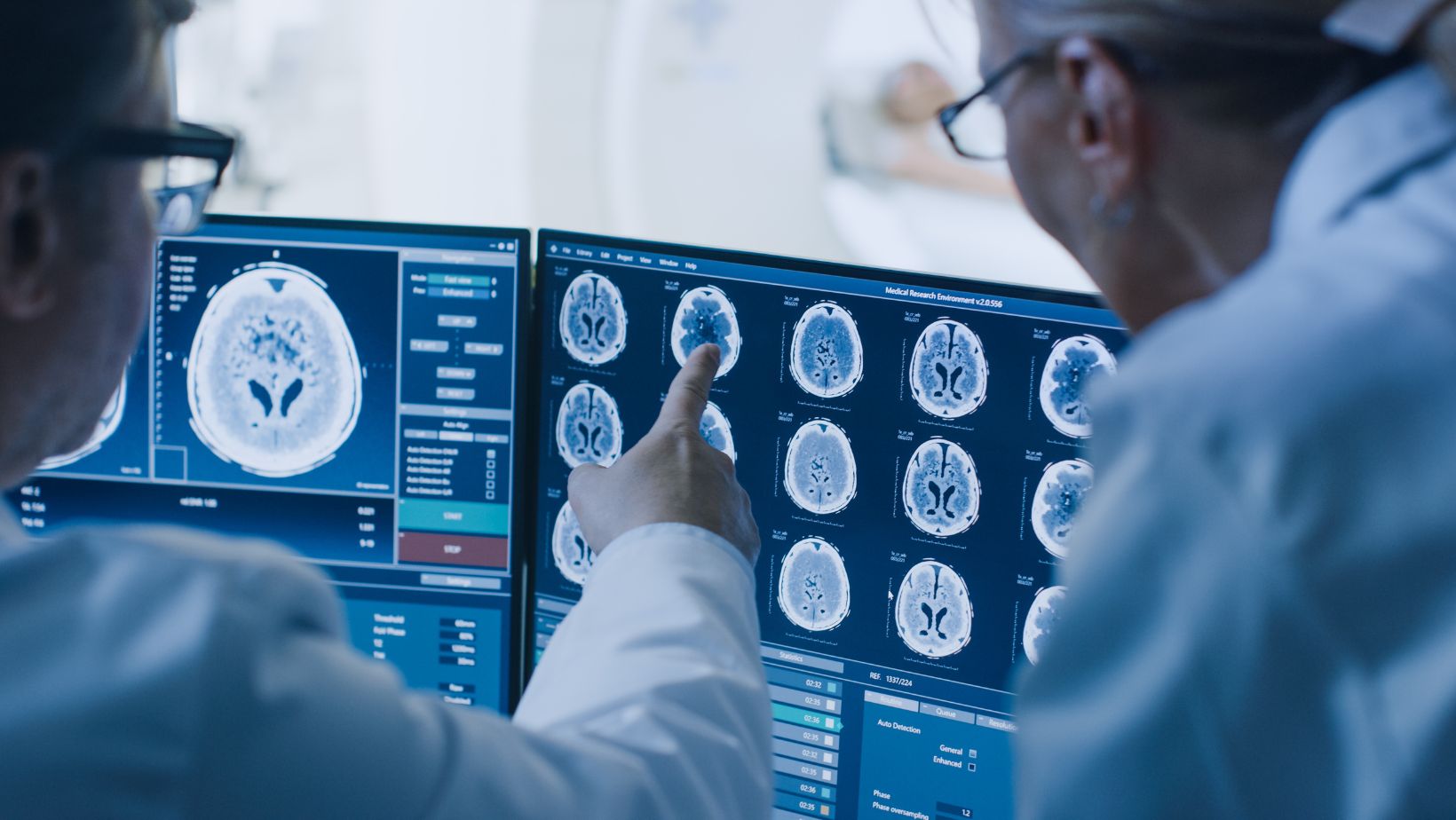
Each type can be used in different situations and contexts, which leads to more precise and adaptable AI apps in healthcare.
Benefits of Custom Image Annotation
Custom image annotation offers several advantages for healthcare:
Improved Diagnostics
AI, trained on annotated datasets, can detect conditions more accurately. This reduces diagnostic errors.
Faster Treatment Decisions
Annotated images provide insights quickly, helping you plan treatments faster.
Accelerated Research and Innovation
Annotated datasets speed up research. They support advanced diagnostic tools and therapies.
Standardized Interpretations
Custom annotations guarantee consistent analysis across teams, hospitals, or research institutions.
Scalable AI Training
With detailed annotations, models can handle complex datasets. It prepares them for real-world use.
These benefits make image annotation services a must for any healthcare organization adopting AI.
Real-World Custom Image Annotation Applications
Custom image annotation is already impacting healthcare. Here are some common use cases:
- Cancer Detection. Annotated mammograms train AI to detect breast cancer early. AI also helps to detect lung cancer through CT scans.
- Annotated MRI Scans. They can help find early signs of Alzheimer’s, MS, and brain tumors. They help with timely interventions.
- Cardiology. AI models trained on labeled echocardiograms can find heart diseases, like valve defects and cardiomyopathies.
- Diabetic Retinopathy. AI can spot signs of diabetic retinopathy in retinal images. This can prevent vision loss with timely treatment.
- Pandemic Preparedness. During COVID-19, annotated CT scans and X-rays helped AI detect and monitor the disease.
- Pediatric Care. Annotated pediatric radiology data helps detect conditions like hip dysplasia. It ensures early intervention.
These examples show you how annotated datasets improve diagnostics and patient care.
Automation in Medical Image Annotation
Manual annotation takes time, but automation helps bridge the gap. AI-powered tools can pre-annotate images, so you can just review and refine the results.
Key features of automated annotation:
- Active Learning. AI models find uncertain areas in an image. They prioritize these for manual review, optimizing your resources.
- Annotation Assistance. Professional tools provide preliminary labels, reducing your workload.
- Scalability. Automation helps medical groups process large datasets. It improves the quality of research.
Combining automation with human expertise saves time. It maintains high-quality annotations.
Future Trends in Image Annotation for Healthcare
Custom image annotation solutions will continue to evolve. Key trends include:
3D and Multimodal Imaging
Better annotation techniques will support 3D imaging. They will combine MRI, CT, and PET scan data for a complete analysis.
Federated Learning
AI models trained on decentralized datasets will enable collaboration without compromising patient privacy.
Improved Annotation Tools
Tools will become more user-friendly, allowing radiologists to annotate faster and more accurately.
Real-Time Annotation
Linking with medical devices may allow quick notes during tests.
This could speed up decision-making.
Quality Control with AI
Advanced systems will flag annotation errors, ensuring consistent dataset quality.
These trends show the ongoing advancement of image annotation in supporting healthcare innovation.
Challenges of Medical Image Annotation and Solutions
Implementing image annotation in healthcare has challenges. But, each can be managed with the right strategies.
| Challenge | Description | Solutions |
| Data Privacy | Protecting sensitive patient information requires strict regulations like GDPR and HIPAA | Use secure, encrypted platforms for data handling. Partner with vendors experienced in healthcare compliance |
| Specialized Expertise | Annotation tasks need skilled radiologists or domain experts | Combine domain expertise with user-friendly annotation tools. Use hybrid workflows with automation |
| Data Complexity | Medical images have subtle features that are hard to annotate accurately | Provide detailed guidelines and training for annotators. Use AI-assisted pre-annotations. |
| Dataset Bias | Lack of diversity in datasets can lead to biased AI models that underperform on certain populations | Source diverse datasets from multiple regions and demographics. Regularly audit models for bias |
| Scalability | Manually annotating large datasets is time-consuming and resource-heavy | Automate repetitive tasks using active learning. Scale operations by outsourcing to professional annotation services |
Conclusion
Custom image annotation is key for AI in healthcare. It powers diagnostic tools and improves patient care. These solutions help you maximize AI in healthcare. They tackle issues like privacy and data complexity.
As automation and innovation advance, the future of annotated medical imaging looks bright. Investing in custom solutions now can greatly improve both healthcare providers and patients.
